
(Adapted from : Capitalism and the catastrophe of environmental pollution)
Using the latest achievements of science and technology to increase labor productivity is a twin phenomenon of capitalism, so that without it there will be no accumulation and as a result, the death of the system will be accelerated. These words certainly has nothing to do with Karl Kautsky´s statement and his inaccurate theory of the deterministic surrender of capitalism to socialism. The grave of capitalism wouldn´t be digged merely because of its historical degeneration and decay, but only by the power of the class struggle of the conscious working masses, organized in nationwide anti-capitalist councils, and ready for socialist planning for work, production and social life. But our discussion here is something else. Capitalism commits any crime for its own survival. Every day we see that capitalism centimeter by centimeter on the planet is laying off millions of workers and closing factories and work centers, mobilization of Nazi and fascist armies, creating war between the working masses around the world and creating a fictitious enemy with the aim of launching imperialist and local wars and mass murder of human beings, that so far to bring its today to tommorow. Capital does all this to survive, and it shouldn´t be imagined that capital´s resorting to these atrocities isn´t dedicated only to times of crisis. It´s a misconception to assume that this system doesn´t destroy anything during the economic prosperity, doing constantly increasing the intensity of exploitation, incitement to war and genocide and in short and destruction of mankind. The latest achievement of this system, which emerged from the heart of the Second Imperial War is nuclear weapons and nuclear energy reactors. We´re not talking about nuclear weapons because we all know the purpose and outcome of their use without question. But the short history of decades of nuclear energy shows what kind of gift this is. Every decade since the Second Imperial War, there have been between 5 and 6 nuclear accidents in the world. The main trend of these events has been the continuous intensification of the power of destruction and increase of the dimensions of disasters ( note that giving the title of the incident to these is fundamentally wrong because an accident by definition is an event that occurs due to natural forces and beyond human control. If the explosion of a nuclear reactor isn´t an accident but it´s a phenomenon that lies withing it as war is the twin of the class system ). September 29, 1957, Mayak incident took place in the former Soviet Union. Radioactive waste stored in underground tanks, due to the failure of the cooling system, it caused the tankers to gradually rise in temperature and finally exploded. The radioactive material (Plutonium) released from the explosion was released to the ground at a height of one kilometer and a radius of 30-50 kilometers. the incident was considered one of the largest nuclear events on an international scale (INES: the International Nuclear Event Scale) and was marked with a grade of 6 in the grading system from 1 to 7. ( look at figure 10 ). In October 1957, a fire broke out at a British nuclear reactor in Sellafeild, causing the release and spread of radioactive material. It was the largest accident of its kind before Chernobyl. The amount of radioactive scattering that contaminated milk, poultry, livestock and lakes was estimated at 11 tonnes of uranium. March 1979, an explosion at the Harrisburg nuclear facility causes so much pollution in the surrounding area that the routine clearing of the area of emitted radioactivity took up to 5 years. The catastrophe was such that the permanent shutdown of the reactors in this complex followed.
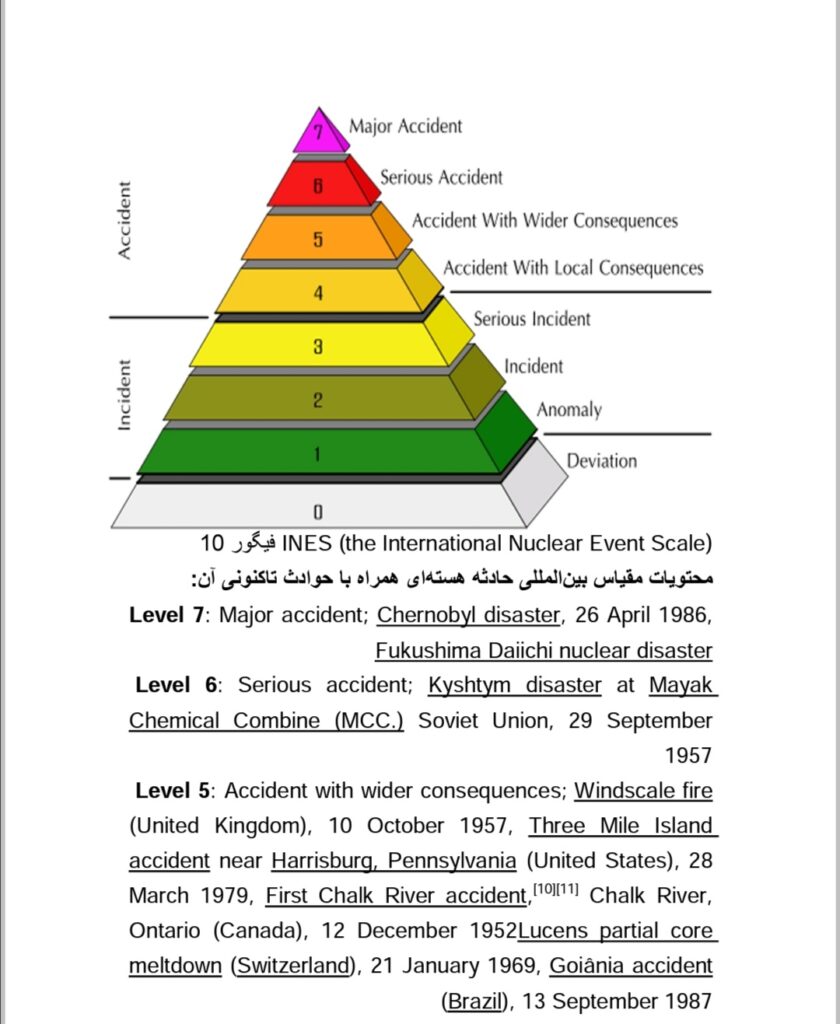


April of the year 1986, the famous Chernobyl accident happened in Ukraine. This country was part of the former Soviet Union at the time. One of the plant´s reactors exploded, and sending radioactive material through much part of Europe and the Soviet Union by wind. The dimensions of this incident were such that the devices for measuring the amount of radioactive materials were not able to record their amount. According to official former Soviet statistics, workers and technicians worked to shut down and cool other reactors, 134 people contracted deadly diseases caused by radioactive effects and 50 of them died soon after. The casualties of this horrific event were estimated in international reports, forecasts and estimates of between 1000 and 1,000,000. At the end of 1986, the whole reactor was blocked in 250 tons of concrete to prevent further radioactive release. A 30-kilometer radius was closed to trafic and this area has been declared dangerous for hundreds of years. The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates the death toll in the city of Kyiv at between 4000 or 5000, and in other parts of Ukraine and Europe at 93,000, but Russian researchers put the number at 1,000,000 across Europe. Following this event, Tyroid Cancer increased dramatically in Ukraine and Belarus and by 2005, about 6,000 people had been treated for the diseases. The last major nuclear accident in Fukushima in March 2011 was due to an earthquake in the eastern waters of Japan. Three of six nuclear reactors were shut down immediately within a few days and began to raise heat and release radioactive material into the air, water and earth. According to the Japan Atomic Protection Agency (NISA), the amount of radioactive material released (Cesium) into air after the incident was 168 times of the Hiroshimma atomic bomb at the end of the Second Imperial War. The Fukushima incident has been the largest incident of its kind in the world to date. (Grade 7 on the scale INES) It was mentioned above that the destructive dimensions of this type of incident are constantly increasing, and their occurrence is also part of the process of producing this type of energy. Extraction of electricity through nuclear processes is one of the cheapest techniques. To explain this, we make a comparison with the production of electricity by oil. In the United States, 790 terawatt hours (TWh) of electricity are generated annually by 100 nuclear reactors. This is the equivalent of electricity, which requires 300 million barrels of oil to produce. The cost of generating electricity from nuclear fuel, including the purchase of radioactive materials, the cost of storing radioactive waste, the cost of nuclear facilities ( imposed on the electricity generation unit ), the cost of destroying reactors at the end of their useful life, the cost of workers´ wages, the technicians and guards, and finally the huge items of profit that the capitalists in this sector of energy production are making. At present, the price per unit of electricity generated by nuclear energy is between 3 and 11 cents per kilowatt hour on the market. Noe if we multiply American´s annual nuclear power generation by 10 cents, it would be about 66 billion dollars, now, if 300 million barrels of oil in the market, including 100 dollar per barrel, becomes 30 billion, and this is just the price of the raw materials needed to produce the desired volume of electricity. To get proper comparison between the production costs of these two types of energy, there must be other very large items, such as the price of labor power, the huge unpaid labor mass of the exploited working masses in this sector, astronomical salaries of specialists and consultants, managers and researchers and holders of similar positions, permanent and circulating costs of fixed capital to be invested ( apart from raw materials ) and add to that 30 billion mentioned above. A calculation that will surely confront us with the higher cost of oil-based electricity compared to its nuclear equvalent. Concentration of nuclear facilities together, easy access to raw materials such as plutonium or uranium, lack of complexity of the technique used compared to other energy techniques and finally, most importantly, its high productivity and efficiency compared to other energy sources has made it grow faster than other electricity generating companies. Its biggest and perhaps only weakness is its security protection system. Meanwhile, the reactor cooling and control system has a high sensitivity and weakness. But now, long ago, cooling and control systems with higher reliability have emerged. the problem is that these techniques remain at the research level and in research institutes because their very high cost doesn´t attract any capital. This means that the high efficiency of work in this technique, which is the most important indicator of its superiority over other energy sources, due to the high cost of this system, most of it loses its attractiveness and credibility. Apart from the mentioned events, two other risky trends always accompany the production of nuclear energy. One is the extraction of raw materials to produce ingot of radioactive materials which from the very beginning, that is, the beginning of the mining process, threatens the living environment of the workers and technicians. Unfortunately, due to the very complex secrecy that exists due to the possibility of producing nuclear weapons in this area, there´s little information available on the extent of environmental and human degeneration of this energy production. The second risk is radioactive waste due to the use of radioactive elements. As for this waste, it has been said so far that it´s kept in heavy water pools inside the nuclear power plant for up to a year after collection and then stored in other pools for 40 to 50 years and finally, after this period, the pulp is stored at a depth of at least 500 meters in the ground and in isolated reservoirs for at least a thousand years and after this period, their radioactive rays end. It should be noted that even after this period, it ends with the emission of direct radioactive radiation, but these substances are still harmful to the environment and to animals. Therefore, they must be stored in closed underground tanks for 100, 000 years. It has happened many times that these materials have leaked out of their barrels and tanks and have polluted groundwater. The process of assigning nuclear waste isn´t followed by the manufactures as above, and it has often happened that radioactive waste is transported to other countries, including Africa, where it´s stored in unsuitable places near workers´ residential areas. It should be noted too that according to international atomic energy law, the transportation of this waste to other countries is completely legal, provided that the host country has the necessary laws, responsible institutions and level of technique. It´s precisely because of this level of technique and the laws of the host countries that companies and governments producing nuclear waste dump this waste wherever they want at a relatively free price. The same is true of the production of radioactive elements used in nuclear energy. This means that the productive capitalists produce and sell these materials in the international mmarket at cheap prices and almost free labor power without observing the minimum working and living conditions of the workers of these countries .
Hassan Abbasi
Oct. 2014





